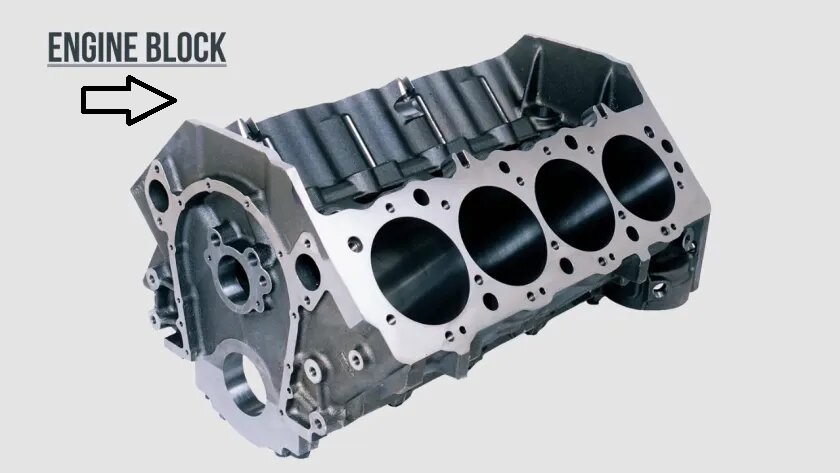

The foundation of the engine that houses cylinders and supports essential engine components.

Seals the top of the cylinders, housing intake and exhaust valves for combustion.
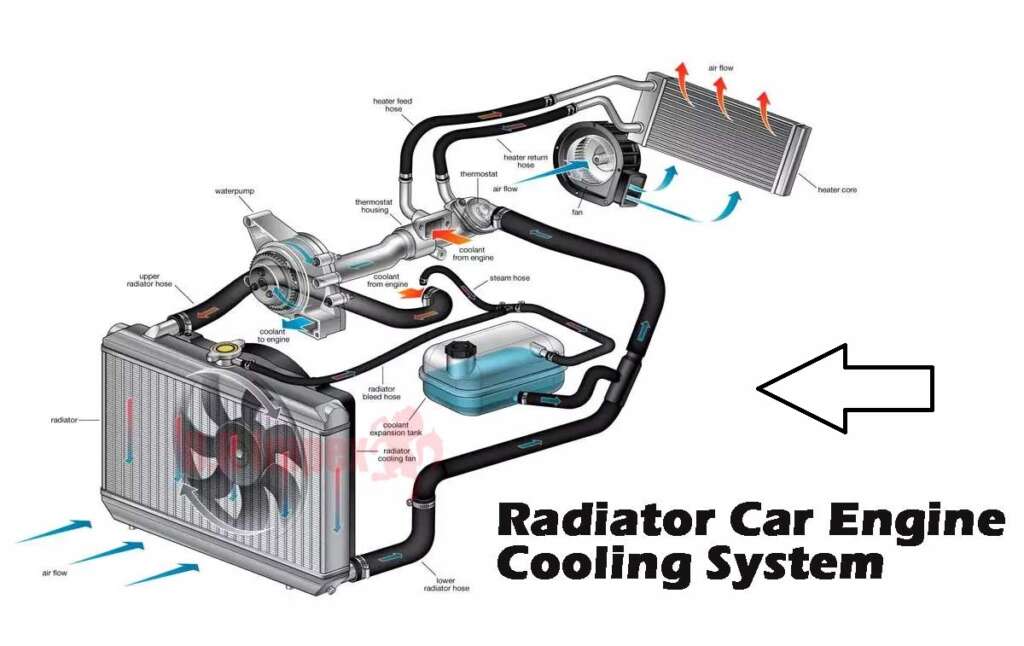
Dissipates heat from the engine coolant to prevent overheating.
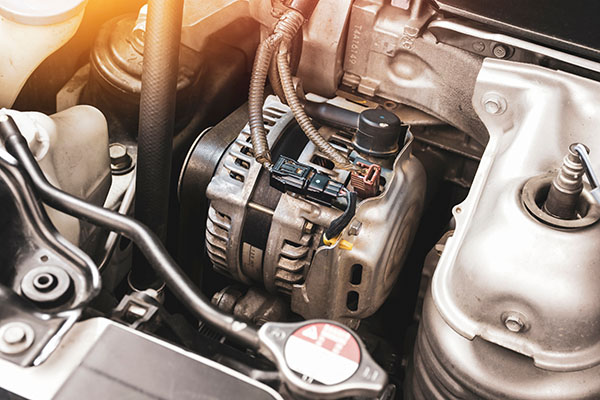

Generates electricity to charge the battery and power electronic components.

Reduces harmful exhaust emissions by converting them into less toxic substances.

Circulates oil under pressure to lubricate engine parts and cool them.

Timing Belt: Synchronizing Engine Functions for Smooth Operation
Maintains coordination between the crankshaft and camshaft movements.

Sprays fuel into the combustion chamber for optimal combustion efficiency.

Air Filter: Protecting Your Engine from Dirt and Debris
Filters air entering the engine, ensuring clean airflow for combustion.

Press against brake rotors to slow down or stop the vehicle.

Engages and disengages power flow between the engine and wheels.

Spins the engine to start combustion when you turn the key.

Collects exhaust gases from cylinders and channels them to the exhaust system.

Shock Absorbers: Reducing Impact for a Smoother Ride
Absorb shocks from the road, improving comfort and vehicle handling.

Control Arm: The Link Between Suspension and Vehicle Frame
Allows controlled up-and-down movement of the wheels.

Differential: Distributing Power to Wheels for Effective Turning
Balances power distribution to wheels, enabling smooth cornering.

Steering Rack: Directing Wheel Movements for Precise Turning
Converts steering wheel rotation into wheel movements.

Battery: Providing Energy to Start the Car and Power Accessories
Supplies electrical power for starting the engine and running electronic systems.

Turbocharger: Boosting Engine Power with Compressed Air
Increases engine efficiency and output by forcing extra air into the combustion chamber.

Fuel Tank: Safe Storage for Vehicle Fuel Supply
Holds and supplies fuel to the engine for combustion.

