Share This Article
How does the Muffler work in your Car?
1. Introduction
When you start your car, the engine generates a series of rapid explosions that create energy to power the vehicle. These combustions produce not only exhaust gases but also significant noise. Without a proper system to manage this sound, driving would be extremely loud and disruptive. This is where a key component of the exhaust system plays its role—designed to minimize noise and ensure smooth airflow while maintaining engine efficiency.
Beyond noise reduction, this essential part of the exhaust setup contributes to overall vehicle performance. It helps regulate the flow of gases leaving the engine, balancing backpressure to optimize fuel efficiency and power output. A well-maintained system enhances driving comfort, prevents excessive emissions, and ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
Understanding how this component functions can help drivers make informed decisions about maintenance, upgrades, and potential modifications. Whether you’re looking to improve engine performance, enhance the driving experience, or simply ensure longevity, knowing the inner workings of this part is crucial. This article will break down its role, working principles, different types, and its impact on vehicle performance in an easy-to-understand manner.
2. What is a Muffler?
Definition and Basic Function
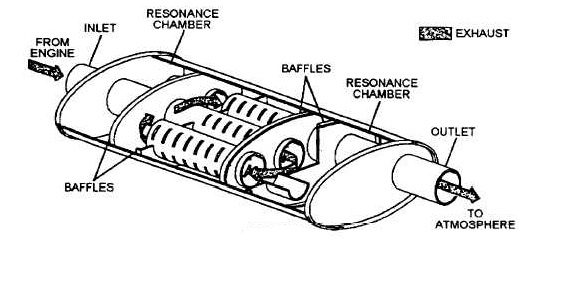
A vehicle’s exhaust system is responsible for directing combustion gases away from the engine, but without the right components, this process can be extremely noisy. One key element helps control sound levels by dampening the pressure waves created during fuel combustion. It is designed with internal chambers or perforated tubes that disrupt and absorb sound energy, making the vehicle quieter while ensuring efficient gas flow. Additionally, it plays a role in maintaining optimal engine performance by managing airflow and back pressure.
Location in the Exhaust System
This noise-reducing component is positioned along the exhaust pipeline, typically toward the rear of the vehicle. As gases exit the engine through the manifold, they pass through the catalytic converter, which helps reduce emissions. From there, they travel through the resonator (if equipped) before reaching the sound-dampening unit, where noise reduction takes place. Finally, the treated gases exit through the tailpipe. Its placement ensures that harmful emissions are processed properly while keeping engine noise at acceptable levels.
Common Materials Used in Construction
To withstand high temperatures and exposure to moisture, this component is typically made from durable metals. Stainless steel is a popular choice due to its resistance to corrosion, ensuring longevity even in harsh weather conditions. Aluminized steel offers a more cost-effective alternative with decent rust protection, while titanium is used in high-performance applications for its lightweight properties. Inside, sound-absorbing materials such as fiberglass or steel wool help further reduce vibrations and unwanted noise. The combination of these materials ensures durability and efficient operation throughout the lifespan of the vehicle.
3. The Role of a Muffler in a Car’s Exhaust System
How It Interacts with Other Exhaust Components
A vehicle’s exhaust system is a complex network of parts working together to manage engine emissions, noise levels, and overall performance. The process begins at the exhaust manifold, where gases from the engine’s cylinders are collected and directed toward the catalytic converter. This crucial component reduces harmful pollutants before the gases continue through the resonator, which helps fine-tune sound frequencies. As the gases move further down the system, they pass through the sound-dampening chamber, where pressure waves are dispersed to reduce noise before exiting through the tailpipe. Each part plays a specific role, ensuring that exhaust flow remains efficient while keeping noise and emissions within acceptable limits.
The Journey of Exhaust Gases from Engine to Tailpipe
Combustion within the engine produces high-pressure gases that must be safely expelled. These gases first travel through the manifold, which channels them into a single stream. The catalytic converter then processes the emissions, breaking down harmful substances such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. If the vehicle has a resonator, it further refines the sound frequencies before the gases enter the noise-reduction chamber. Here, internal baffles, perforated tubes, and sound-absorbing materials work together to minimize engine noise without restricting airflow. Once processed, the gases make their final exit through the tailpipe, completing the cycle.
Contribution to Emissions Control and Efficiency
While its primary function is noise reduction, this exhaust component also plays a role in maintaining engine efficiency. By regulating airflow and backpressure it helps optimize combustion performance, which can have an impact on fuel economy. A well-functioning system prevents unnecessary restrictions that could force the engine to work harder, leading to excessive fuel consumption. Additionally, modern designs work in harmony with emissions-control devices, ensuring that pollutants are effectively processed before being released into the environment. Proper maintenance of this system helps extend the lifespan of related components while keeping the vehicle compliant with environmental regulations.
4. How Does a Muffler Work?
Sound Reduction Mechanism
When an engine runs, it generates intense pressure waves due to the rapid combustion of fuel and air. These waves travel through the exhaust system as pulsating noise, which, if left uncontrolled, would result in an extremely loud driving experience. The sound-dampening unit is engineered to counteract this effect by using a combination of chambers, perforated tubes, and sound-absorbing materials. By redirecting and disrupting the pressure waves, it effectively minimizes harsh engine noise before the gases exit through the tailpipe.
Explanation of Sound Waves and Noise Cancellation
Sound waves behave in a pattern of compressions and rarefactions, and the key to reducing noise lies in canceling out these waves. Inside the noise-controlling unit, carefully designed chambers create a system of interference where sound waves reflect and collide with each other. This process, known as destructive interference, helps neutralize excessive vibrations, resulting in a quieter output. Some models use resonating chambers that are tuned to specific frequencies, further eliminating unwanted noise while preserving a deep, refined exhaust tone.
Use of Chambers, Perforated Tubes, and Sound-Dampening Materials
To achieve efficient noise reduction, manufacturers incorporate a combination of design elements. Chambers are strategically placed to reflect and disperse sound waves, while perforated tubes help regulate the passage of exhaust gases. Many designs also utilize materials such as fiberglass, steel wool, or ceramic composites, which absorb excess sound energy and vibrations. This blend of structural engineering and acoustic science ensures that noise is controlled without excessively restricting exhaust flow.
Backpressure and Performance
Beyond noise reduction, a well-designed exhaust silencer also plays a role in regulating airflow. As exhaust gases move through the system, a certain amount of backpressure is created—this resistance helps maintain optimal exhaust velocity, ensuring the engine operates efficiently. However, excessive restriction can negatively impact performance, limiting horsepower and fuel economy.
The Balance Between Noise Reduction and Engine Efficiency
A delicate balance must be maintained between quiet operation and engine output. Factory-installed designs focus on maximum noise suppression while keeping airflow at an acceptable level for daily driving. Performance-oriented models, such as straight-through or high-flow variants, prioritize reduced restrictions to enhance horsepower and throttle response. The choice of design depends on the driver’s preference—whether they prioritize quiet operation, fuel efficiency, or increased engine power. Proper selection and maintenance of this component ensure optimal vehicle performance while keeping noise within legal limits.
5. Types of Mufflers and How They Differ
The design of an exhaust silencer plays a crucial role in determining a vehicle’s sound characteristics, airflow efficiency, and overall performance. Various types are available, each engineered with different internal structures to meet specific driving needs. From noise suppression to performance enhancement, the right choice depends on factors such as vehicle type, engine specifications, and personal preferences.
Chambered Mufflers
Chambered designs, such as those from Flowmaster, use a series of internal compartments to manage sound waves effectively. As exhaust gases pass through the chambers, sound waves bounce off the walls and interact with each other. This process creates destructive interference, which cancels out specific frequencies while enhancing a deep, aggressive tone. The design offers a balance between noise control and performance, making it a popular choice among muscle car and truck owners who want a throaty exhaust note without excessive restriction.
Straight-Through
Also known as glass packs, straight-through designs prioritize minimal exhaust restriction to maximize airflow. They consist of a perforated core wrapped in sound-absorbing material, such as fiberglass, allowing gases to pass with minimal resistance. This results in a louder, more aggressive exhaust note and improved horsepower output, making them a favorite for performance enthusiasts. However, since they provide less noise reduction than other types, they may not be ideal for drivers seeking a quieter ride.
Turbo Mufflers
Turbo-style exhaust silencers use an internal setup of perforated tubes arranged in an S-shaped or multi-pass design. This configuration forces gases to travel through multiple passages, reducing noise while still allowing reasonable airflow. Compared to chambered and straight-through designs, turbo models offer a quieter and more refined sound, making them a great choice for everyday vehicles where comfort and efficiency are priorities. The multi-pass design also helps improve backpressure balance, contributing to better fuel economy.
Performance vs. Stock Mufflers
Factory-installed silencers are designed primarily for noise suppression and emissions compliance, often restricting airflow to meet regulatory requirements. While they ensure a smooth and quiet ride, they may slightly limit engine efficiency. In contrast, performance-oriented alternatives, such as high-flow or straight-through designs, reduce restrictions to enhance horsepower and throttle response. The trade-off is often a louder exhaust note, which can vary depending on the internal structure. Choosing between stock and aftermarket options depends on whether the driver prioritizes comfort, fuel efficiency, or increased power output.
Each type offers distinct advantages, and selecting the right one depends on driving goals and vehicle specifications. Whether optimizing performance, enhancing sound, or maintaining a quiet ride, understanding these differences helps in making an informed decision.
6. The Science Behind Noise Cancellation in Mufflers
A vehicle’s exhaust system generates powerful sound waves due to combustion inside the engine. Without proper noise control, the result would be an unbearably loud driving experience. To manage this, advanced engineering principles are applied within the exhaust silencer, utilizing wave interference, specialized chambers, and sound-absorbing materials to reduce unwanted noise while maintaining performance.
Sound Wave Interference and Noise Cancellation Principles
Noise reduction in an exhaust silencer primarily relies on the principle of destructive interference. When sound waves travel through the exhaust system, they can either amplify or cancel each other out, depending on how they interact. By designing the internal structure to reflect and manipulate these waves, engineers create conditions where high and low-pressure zones collide, effectively neutralizing excessive noise. Some models also incorporate Helmholtz resonance chambers, which are tuned to specific frequencies to eliminate harsh sounds while preserving a deep, refined exhaust note.
Role of Baffles, Resonating Chambers, and Absorption Materials
Different designs use a combination of physical barriers and acoustic materials to achieve sound suppression:
- Baffles: These are strategically placed metal plates that redirect exhaust flow, forcing sound waves to change direction multiple times. This scattering effect disrupts wave energy, reducing noise output.
- Resonating Chambers: These specially tuned compartments create counter-waves that cancel out specific frequencies, helping to refine the exhaust note. They are often used in high-performance and luxury vehicles to maintain a pleasant sound profile.
- Absorption Materials: Components such as fiberglass, ceramic wool, or stainless steel mesh absorb sound energy as gases pass through. These materials are particularly effective in straight-through designs, where they reduce high-frequency noise without significantly restricting airflow.
Differences Between OEM and Aftermarket Mufflers in Sound Control
Factory-installed exhaust silencers (OEM) prioritize noise reduction and emissions compliance, often using complex chamber designs and dense soundproofing materials to create a smooth and quiet driving experience. These models are engineered to meet regulatory standards while ensuring comfort for everyday driving.
In contrast, aftermarket options cater to various performance and sound preferences. Some high-flow designs reduce restrictions to improve horsepower but may produce a louder exhaust note. Others focus on aggressive tuning, using resonating chambers and minimal baffles to enhance the deep rumble often desired in sports cars and trucks. The key difference lies in the balance between sound control and performance enhancement, allowing drivers to choose an option that suits their specific needs.
7. Signs of a Failing or Damaged Muffler
Over time, components in the exhaust system can deteriorate due to exposure to heat, moisture, and road debris. A malfunctioning silencer can lead to increased noise, decreased fuel efficiency, and even safety hazards. Recognizing early warning signs can help prevent costly repairs and ensure a smooth driving experience.
Increased Noise Levels – What Unusual Sounds Indicate
One of the first signs of a failing exhaust silencer is a noticeable increase in engine noise. If the vehicle starts producing a deep, rumbling sound or a rattling noise, it could indicate internal damage. Holes, cracks, or a broken baffle can prevent the proper dampening of sound waves, making the vehicle louder than usual. A sudden change in exhaust tone should not be ignored, as it may suggest structural wear that needs immediate attention.
Reduced Fuel Efficiency – How Leaks and Blockages Affect Mileage
An efficiently functioning exhaust system helps maintain optimal backpressure, which contributes to fuel economy. When leaks develop, or internal obstructions form, the engine has to work harder to expel gases, leading to increased fuel consumption. Drivers may notice a decrease in miles per gallon (MPG), especially during acceleration or highway driving. If fuel efficiency drops unexpectedly, an inspection of the exhaust system is recommended to identify possible leaks or restrictions.
Exhaust Fumes Inside the Car – Why This Is a Serious Issue
A properly sealed exhaust system directs harmful gases away from the vehicle, but a damaged section can cause toxic fumes, including carbon monoxide, to leak into the cabin. This poses a serious health risk, as exposure to these gases can lead to dizziness, headaches, and, in extreme cases, carbon monoxide poisoning. If there is an unusual smell of exhaust inside the car, it is critical to stop driving and have the system inspected immediately.
Visible Rust or Damage – How to Inspect Your Muffler
Regular visual inspections can help detect early signs of wear and corrosion. Rust, cracks, or physical damage on the outer shell indicate possible structural weakness. Additionally, moisture buildup inside the system can accelerate rust formation, leading to holes that affect both noise control and exhaust flow. Checking for loose or hanging parts under the vehicle can also reveal mounting issues that need attention. Addressing rust and damage early can extend the lifespan of the exhaust system and prevent more severe mechanical failures.
Recognizing these warning signs early can help maintain engine performance, fuel efficiency, and overall driving safety. Regular maintenance and timely repairs ensure a properly functioning exhaust system, keeping both the vehicle and its passengers safe on the road.
8. How to Maintain and Extend the Life of Your Muffler
A well-maintained exhaust system ensures efficient performance, reduces emissions, and prevents costly repairs. Since this component is constantly exposed to heat, moisture, and road debris, taking preventive measures can significantly extend its lifespan. Regular care helps avoid rust, blockages, and other issues that could impact vehicle performance.
One of the most common causes of premature wear is rust formation due to moisture buildup. To prevent this, driving longer distances occasionally helps evaporate trapped condensation inside the system. Additionally, applying a high-temperature rust-resistant coating can provide extra protection against corrosion. Parking in a dry, covered area also helps minimize exposure to moisture, especially in humid or snowy regions where road salt accelerates rusting.
Routine inspections and professional servicing play a key role in detecting minor issues before they become major problems. Checking for visible rust, cracks, or loose connections underneath the vehicle can help identify early signs of deterioration. If unusual noises, excessive emissions, or reduced fuel efficiency are noticed, a professional exhaust check-up is recommended. Mechanics can assess internal components, weld small leaks, and ensure proper alignment to maintain optimal performance.
Fuel quality and driving habits also impact the longevity of exhaust components. Using high-grade fuel reduces carbon buildup inside the system, preventing blockages that could restrict airflow. Additionally, avoiding frequent short trips where the engine doesn’t reach optimal temperature helps prevent excessive moisture retention, which leads to rust formation. Driving smoothly and avoiding sudden accelerations reduces stress on the system, ensuring efficient exhaust flow and prolonged durability.
9. How a Muffler Affects Car Performance
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in engine efficiency, and its noise-dampening component contributes to both sound control and vehicle performance. Many car enthusiasts wonder whether modifying or removing it can enhance horsepower. While such modifications can affect exhaust flow, they also come with potential drawbacks, including increased noise and legal concerns.
Does Removing a Muffler Increase Horsepower?
In theory, eliminating restrictions in the exhaust system can improve airflow, potentially leading to a small gain in power. However, the impact depends on the engine design and overall exhaust setup. In most modern vehicles, removing the silencer alone does not result in significant horsepower gains because the catalytic converter and resonator still regulate exhaust flow. Additionally, many engines rely on a certain level of backpressure for optimal performance. Completely removing the component may cause an imbalance in exhaust velocity, sometimes leading to reduced low-end torque rather than noticeable power improvement.
Pros and Cons of a Muffler Delete
A muffler delete is a modification where the factory-installed noise suppressor is removed and replaced with a straight pipe. This alters the exhaust note, making the vehicle significantly louder.
Pros:
- Produces a more aggressive and sporty exhaust sound.
- May slightly improve exhaust flow in some cases.
- Reduces vehicle weight by eliminating a bulky component.
Cons:
- Increased noise levels, which may be illegal in some regions.
- Potential loss of low-end torque due to reduced backpressure.
- Can negatively affect fuel efficiency and emissions compliance.
- May lead to unwanted drone inside the cabin at certain RPMs.
While some high-performance vehicles may benefit from exhaust modifications, most daily drivers will not see substantial gains from removing the factory silencer.
How Muffler Modifications Impact Emissions Compliance
Emissions regulations are strictly enforced in many countries, and altering the exhaust system can lead to non-compliance. Factory silencers are designed to work alongside catalytic converters to reduce harmful pollutants. Removing or modifying them improperly may increase emissions, potentially causing a vehicle to fail inspection. Additionally, certain modifications can trigger check engine lights due to changes in exhaust backpressure, affecting sensor readings.
10. Common Myths and Misconceptions About Mufflers
Exhaust systems are often misunderstood, leading to widespread myths about their function, performance impact, and legality. Many drivers assume that making modifications—such as installing a louder system or removing it entirely—will automatically improve horsepower or fuel efficiency. However, these beliefs are not always accurate. Understanding the truth behind these misconceptions can help vehicle owners make informed decisions.
Myth: Louder Mufflers Always Mean More Power
A common assumption is that a louder exhaust note indicates a more powerful engine. While some high-performance vehicles produce a deep, aggressive sound due to their tuned exhaust systems, loudness alone does not equal increased horsepower. The primary role of this component is to control sound waves and backpressure, ensuring optimal engine performance. Simply swapping a stock unit for a louder aftermarket option does not guarantee more power unless the entire exhaust system is tuned for efficiency, including proper airflow balance and fuel management adjustments.
Myth: Muffler Deletes Are Legal Everywhere
Some car enthusiasts believe that removing the factory silencer is legal in all areas, but this is far from true. Noise regulations vary by country, state, and even city, with many regions imposing strict limits on exhaust sound levels. In some places, a muffler delete can result in fines, failed inspections, or restrictions on vehicle registration. Additionally, certain modifications can violate emissions laws, as changes to the exhaust system can impact pollution control. Before performing a delete, it’s crucial to check local laws to avoid penalties and potential legal issues.
Myth: All Performance Mufflers Improve Fuel Economy
While high-flow designs can enhance exhaust efficiency, they do not automatically lead to better fuel economy. Fuel consumption is influenced by multiple factors, including engine tuning, driving habits, and aerodynamics. Some aftermarket options reduce backpressure, potentially improving horsepower and throttle response, but they may also encourage more aggressive driving, which can offset any fuel savings. Additionally, poorly designed or oversized units can disrupt exhaust scavenging, leading to inefficient combustion and increased fuel consumption. Choosing the right setup tailored to the engine’s needs is essential for achieving both performance gains and fuel efficiency.
11. Legal Considerations and Environmental Impact
Exhaust systems play a crucial role in regulating vehicle noise and emissions, ensuring compliance with environmental and traffic laws. Many regions have strict regulations regarding modifications that increase noise levels or alter emissions output. Understanding these legal requirements helps drivers avoid fines and ensures their vehicles remain roadworthy.
Noise Regulations in Different Countries and States
Laws regarding vehicle noise levels vary depending on the country, state, or municipality. Many regions set a maximum decibel limit for road vehicles, with enforcement through routine inspections and roadside checks.
- United States: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and individual state laws regulate noise levels, with some states imposing strict limits. California, for example, has one of the toughest regulations, restricting passenger vehicles to 95 decibels.
- United Kingdom: The UK enforces a noise limit of 74 decibels for standard road vehicles, with penalties for excessively loud exhaust modifications.
- Australia: Most states require vehicles to comply with an 85-decibel limit, and modifications must meet approval standards to remain legal.
- European Union: The EU enforces stringent noise and emissions regulations, with newer vehicles required to meet progressively lower decibel limits to reduce noise pollution.
Drivers who install loud exhaust systems or perform muffler deletes risk fines, failed inspections, and potential restrictions on vehicle registration if their modifications exceed local noise limits.
How Mufflers Help in Emissions Control
While primarily designed to reduce noise, exhaust silencers also contribute to emissions control. They work in tandem with catalytic converters and resonators to manage the flow of exhaust gases, promoting efficient combustion and reducing pollutants. A well-functioning system helps minimize the release of harmful emissions, including:
- Carbon monoxide (CO): A toxic gas that can be harmful in enclosed spaces.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): Contribute to smog formation and respiratory issues.
- Unburned hydrocarbons (HC): Can lead to environmental pollution and health hazards.
A faulty or removed silencer can disrupt this process, increasing emissions output and causing the vehicle to fail environmental inspections. Many jurisdictions require periodic emissions testing to ensure compliance with air quality standards.
Legal Consequences of Tampering with a Car’s Exhaust System
Modifying or removing critical exhaust components without proper approval can lead to legal repercussions. In many countries, tampering with emissions control devices, including silencers, is illegal and subject to penalties. Consequences may include:
- Fines and tickets: Law enforcement can issue fines for excessive noise or emissions violations.
- Failed vehicle inspections: Many areas require emissions and noise testing as part of annual inspections, and a non-compliant vehicle may not pass.
- Warranty voiding: Unauthorized modifications can void manufacturer warranties, leading to costly repairs.
- Increased insurance costs: Some insurers may raise premiums or deny coverage if a vehicle has been modified outside of legal regulations.
To avoid these issues, it’s essential to ensure that any modifications comply with local laws. High-performance, street-legal aftermarket options exist that provide enhanced sound and efficiency without violating regulations. Consulting a professional mechanic and reviewing legal requirements before making changes ensures a vehicle remains compliant and environmentally responsible.
12. Choosing the Right Muffler for Your Car
Selecting the ideal exhaust silencer depends on several factors, including sound preference, performance expectations, and budget. A well-matched system enhances vehicle efficiency, reduces unwanted noise, and ensures compliance with legal regulations. Below are the key considerations to help you make an informed decision.
Factors to Consider: Sound Preference, Performance Goals, Budget
Before purchasing an aftermarket unit, it’s important to determine what you want to achieve:
- Sound Preference: Different designs produce distinct exhaust tones. Some provide a deep, aggressive rumble, while others maintain a quieter, more refined note.
- Performance Goals: High-flow designs can enhance horsepower and throttle response, but they must be compatible with the vehicle’s exhaust system to avoid performance loss.
- Budget: Prices vary based on material quality, design complexity, and brand reputation. While premium models offer superior durability and efficiency, budget-friendly options still provide noticeable improvements.
How to Match a Muffler with Your Car’s Engine and Exhaust Setup
Choosing the right option requires compatibility with the vehicle’s exhaust system and engine type. Consider the following:
- Engine Size and Power Output: Larger engines with higher horsepower benefit from free-flowing designs that reduce backpressure, while smaller engines may require more restrictive options to maintain efficiency.
- Exhaust Pipe Diameter: A mismatch between the silencer and the exhaust pipe can create turbulence or excessive resistance, affecting performance. Ensure the inlet and outlet sizes match your existing setup.
- Driving Conditions: Daily drivers may prefer quieter models with better noise insulation, while performance-focused vehicles can benefit from aggressive-sounding, high-flow units.
Best Muffler Brands and Their Unique Features
Several manufacturers offer high-quality options designed for different driving needs:
- Flowmaster: Known for its chambered designs that deliver a signature aggressive exhaust note, ideal for muscle cars and performance vehicles.
- MagnaFlow: Features straight-through designs that enhance exhaust flow while maintaining a deep, smooth sound. Great for a balance of performance and sound quality.
- Borla: Premium, stainless steel options with a focus on durability and power gains, often used in high-performance and luxury vehicles.
- Walker: Specializes in affordable, factory-style replacements that provide quiet operation and long-lasting performance.
- Cherry Bomb: Famous for its glass pack designs, producing a raw, throaty exhaust tone, often used in custom and classic car builds.
13. Conclusion
A well-functioning exhaust silencer is essential for maintaining a vehicle’s performance, noise control, and emissions compliance. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored its role in the exhaust system, how it reduces sound and enhances efficiency, and the different types available for various driving needs. Understanding its function helps car owners make informed decisions when choosing, maintaining, or upgrading their exhaust setup.
Keeping this component in good condition ensures a quieter, smoother ride while preventing issues like excessive noise, decreased fuel efficiency, and harmful emissions leaks. Regular inspections and timely replacements help extend its lifespan and prevent costly repairs. Whether using a stock or high-performance aftermarket option, ensuring compatibility with the vehicle’s exhaust system is crucial for achieving the best results.
Proper maintenance not only enhances driving comfort but also keeps the vehicle compliant with noise and emissions regulations. By taking proactive steps—such as checking for damage, avoiding rust buildup, and following manufacturer recommendations—drivers can enjoy improved engine performance, reduced environmental impact, and a better overall driving experience.
Is a Muffler a Silencer?
Yes, a muffler is also known as a silencer in many countries, particularly in Europe and Asia. Its primary function is to reduce the noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases. By using chambers, baffles, or perforated tubes, it cancels out or absorbs sound waves, making the vehicle quieter. While “muffler” is the common term in the U.S., “silencer” is frequently used in the UK and India.
Is a Muffler a Catalytic Converter?
No, a muffler and a catalytic converter are two different components in a vehicle’s exhaust system. The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons into less harmful gases before they exit the tailpipe. The muffler, on the other hand, is designed to control noise. While both are part of the exhaust system, they serve separate purposes.
Can My Car Run Without a Muffler?
Yes, a car can physically run without a muffler, but it is not advisable. Removing it results in extremely loud engine noise, which may violate local noise regulations and lead to fines. Additionally, while removing it (a muffler delete) can slightly improve exhaust flow and performance, it can also increase emissions, reduce backpressure efficiency, and negatively impact fuel economy. In some cases, it may even cause damage to other exhaust components over time.
What Are the Benefits of a Car Muffler?
A muffler provides several advantages, including:
- Noise Reduction: Controls and dampens engine sound for a quieter, more comfortable ride.
- Improved Engine Efficiency: Helps regulate exhaust backpressure, optimizing performance and fuel consumption.
- Emission Control Assistance: Works alongside the catalytic converter to ensure proper exhaust flow and compliance with emissions standards.
- Legal Compliance: Keeps the vehicle within noise regulations to avoid fines and failed inspections.
- Enhanced Driving Comfort: Reduces excessive vibrations and unwanted engine noise inside the cabin.


